South Africa don confam dia second death from Mpox, di kontri health ministry announce.
According to di health ministry, di thirty-eight year old man bin dey admitted to hospital for KwaZulu-Natal province wia im bin test positive for di disease and die di same day.
Di first death from di disease na one 37-year-old man wey die on Monday afta dem admit am to one hospital for Gauteng province, na so South Africa health minister Joe Phaahla tok.
Dem don confirm four oda cases for di province, and dis bring di total number of positive cases for di kontri to six.
Di health ministry tok say all di patients na men wey dey for dia thirties and dem neva go oda kontris wey dey experience di outbreak.
Mpox, wey dem bin dey call monkeypox bifor, dey spread through close contact. Most cases dey mild
Initial symptoms include fever, headaches, swellings, back pain, aching muscles, wey fit develop into a rash.
Di World Health Organization (WHO) bin declare public health emergency ova one outbreak of mpox for 2022. Although e end last year, dem still dey report low levels of cases for some kontris.
Anybodi wey come into contact wit di patient wey die go dey monitored for 21 days.
Di first human case happun for Democratic Republic of Congo for 1970 and di disease dey endemic dia, according to WHO.
How Mpox dey spread?
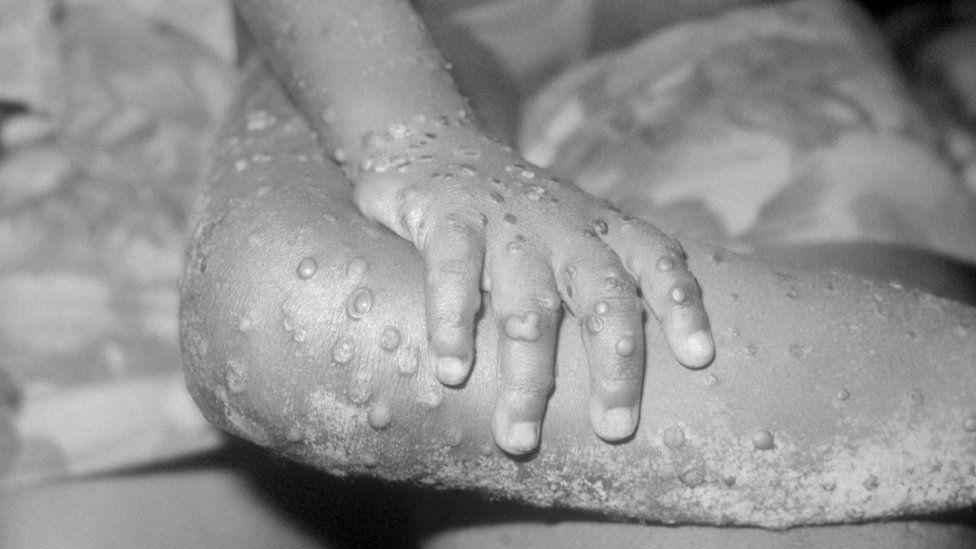
Unlike di virus wey dey cause Covid-19, wey primarily dey spread through tiny droplets wey we dey expel as we breathe wey dey highly infectious, mpox no dey easily transmissible. Mpox dey rely on close physical contact – usually for a long time – to pass from pesin to pesin, or animal to pesin.
“E fit be contact wit somebody wey get an infectious rash, like lesions, scabs and bodily fluids,” na so Madeline Barron, from di American Society for Microbiology (ASM) tok. “You fit also get am by touching items wey somebody wey don dey infected touch.”
Although sabi pipo don detect DNA of Mpox virus for semen, e no necessarily mean say now how e dey spread.
One study wey dem publish for di New England Journal of Medicine find out say between April and June 2022, 98% of di infections for 16 kontris na men wey dey sleep wit men, but e no dey clear why dis na di case.
E fit just be coincidence – once disease enta one community, e dey spread within dat community. And evidence no dey say monkeypox dey pass quicker through a population of men wey dey sleep wit men dan any oda group. Also evidence no dey say men dey catch am pass women.
“We no know if di virus fit spread specifically through sexual transmission routes, like through vaginal secretions or semen, but e be like say intimate contact dey promote di spread,” na so Barron tok.
Although sabi pipodon detect di DNA from mpox virus for semen, e no necessarily mean say dat na how e dey spread.
Di mpox virus na packet of genetic information wey dey inside envelope of proteins and a membrane. E need all these components to work in order to infect cells, and although viral DNA fit dey for semen, di virus itself fit no dey viable and capable of infection.
How to protect your bodi from Mpox
Even though health experts agree say di risks to di public dey low, see several tins you fit do to reduce your risk of catching di virus.
Dis recommendations na from U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, U.K. National Health Service and WHO wey include:
- Avoid contact wit pipo wey recently get di virus or those wey fit dey infected. Wear face mask if you dey in close contact wit someone wey get symptoms.
- Use condom and shine ur eye for symptoms if you recently change your sexual partner. Avoid contact wit animals wey fit carry di virus. Dis include sick or dead animals and particularly those wit history of di infection, like monkey, rodents and prairie dogs.
- Practice good hand hygiene, especially afta you come in contact wit infected — or suspected infected — animals or humans. For example, wash your hands wit soap and water or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Use personal protective equipment wen you dey care for patients wit confirmed or suspected monkeypox infection.
- Only eat meat wey dem cook well-well.